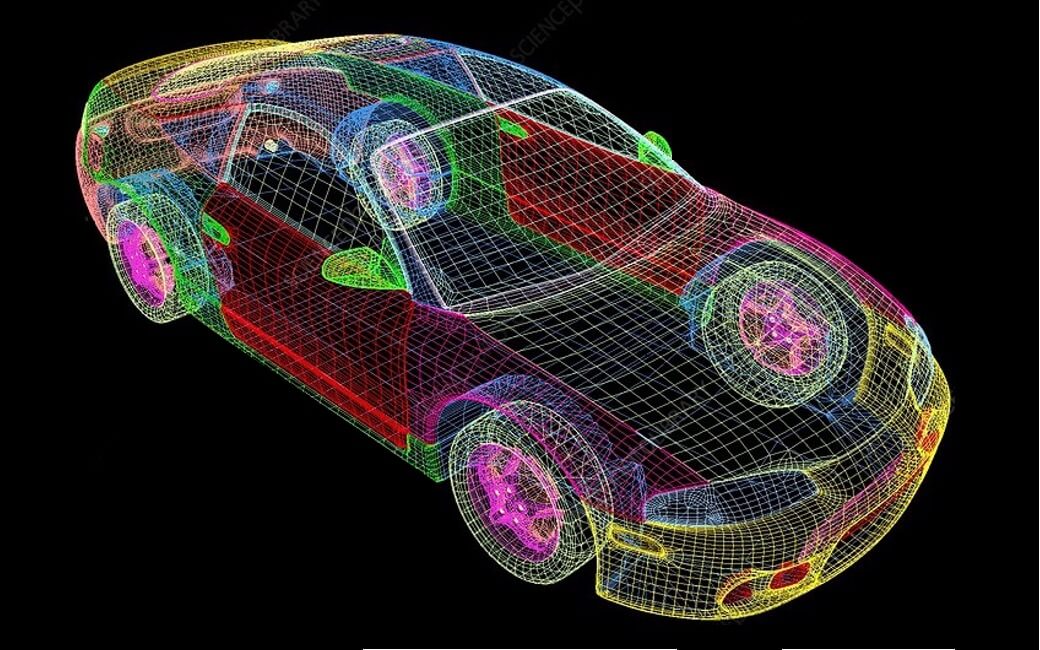
Use of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) along with 3D Printing as Part of Formula 1 car Development
The sound of the engines, the scorching heat on the road, and the excitement of racing. The sound of the engines, the heat of asphalt, and the thrill of winning Formula 1 cars are the ultimate in speed and power. They also have the most ability to move. For many years, Formula 1 has been the most prestigious racing class around the globe and has pushed the limits of engineering with each new version. From the very first Ferrari F1 cars of the 1950s through the current versions of the current day, Formula 1 cars have been the source of much interest and debate.
The motorsports industry is known for its ingenuity and relentless pursuit of excellence, which is why Formula 1 is often a reference point for technological advancements. Teams of researchers and developers trying to develop the most efficient cars using advanced technologies like Computer-aided Design (CAD), as well as 3D printers, are essential to the creation of the Formula 1 car. From allowing teams to design more aerodynamic designs to reducing the amount of time needed to evaluate new components, 3D printing and CAD have revolutionized the development of cars for Formula 1.
The article we’ll look at the importance of 3D printing as well as F1 developing CAD for cars, and how these technologies can improve racing automobiles.
Table of Contents
Exploring the Evolution of 3D Printing Technology in Formula 1 Racing
In the last decade, 3D printing has become a vital part of Formula 1 racing. From the manufacture of parts and components to the creation of new concepts, 3D printing helped transform the sport. The development of 3D printing technologies within Formula 1 over the years has helped teams achieve a competitive advantage by reducing costs, enhancing precision, and decreasing the time-to-market.
- The first time we saw 3D printing for Formula 1 racing was in 2014, when McLaren unveiled their first 3D-printed component for their car, which was a valve cover for the engine. It was printed using the Stratasys 3D printer that utilized the FDM process to produce the complicated component. Since then, 3D printing has become more commonplace within Formula 1 racing, with teams like Ferrari, Renault, and Mercedes all employing 3D printing to create parts and components of their vehicles.
- In 2017, 3D printing made another step forward, with the introduction of revolutionary technology known as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS). The process utilizes the laser to sinter metallic powders into a solid shape that allows the manufacture of intricate parts with the highest levels of precision. This process was utilized by Ferrari to create an aerodynamic element for their car in 2017. This marked the first occasion that a metal component was 3D printed to be used in a Formula 1 car. Since that time, 3D printing technology has been evolving within Formula 1 racing.
- In the year 2019, Renault employed 3D printing to make carbon-fibre brakes to be used in their automobile. It was made by using a method called Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), which enabled the creation of complicated geometries with the highest levels of precision. It was the first 3D-printed carbon-fibre element to be utilized in a Formula 1 car.
- The most recent advancement of 3D printing technology used in Formula 1 racing is the introduction of generative design. This technology employs computer algorithms to create innovative designs that can then be printed in 3D and tested through the test wind-room. This technology was employed in the case of Mercedes for 2020 in order to develop an aerodynamic part for their car. The part was manufactured through a process called Multi Jet Fusion (MJF) that allowed the manufacturing of complicated components with the highest levels of precision.
The advancement of 3D printing technology in Formula 1 racing over the years has been astounding. From the manufacturing of simple components to the creation of innovative designs, 3D printing has helped teams to gain an advantage through lowering costs, improving accuracy, and reducing lead time. While 3D printing continues to advance as it does, more and more teams will be able to make use of the technology in order to get a competitive edge over their competitors.
Examples of CAD and 3D Printing Applications in F1 Car Development
In the past few years, the technology utilized for F1 cars has become more sophisticated, and teams are using the latest Computer-aided Design (CAD) programs and 3D printer programs to build more efficient and powerful race cars.
The design process and function of CAD software are utilized to simulate the race car and optimize its performance. With CAD, engineers are able to quickly make virtual models of their car and then try different designs to find the best solution. This lets them make modifications to the vehicle within a matter of a few minutes instead of taking days or even hours to make physical adjustments. 3D printing technology is employed for F1 automobile development.
3D printing lets teams make complex parts with intricate details and forms that are hard to produce using traditional manufacturing techniques. Through 3D printing technology, companies are able to quickly and easily create parts that are stronger, lighter, and more aerodynamic. These advancements in CAD as well as 3D printing, have enabled F1 teams to design quicker and faster race vehicles.
Through these techniques, teams can design and develop components that are more lightweight, stronger, and more aerodynamic, providing them with an advantage in the race.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing and CAD Car Development
The use of 3D printing and CAD in F1 car development poses many problems and limitations that have to be considered and including the following:
- Cost: The price of 3D printing and CAD techniques may be prohibitive to certain car designers, since the expense of hardware and software could be costly. In addition, the expense of materials used for 3D printing could be costly since some materials that are utilized for 3D printing might not be easily available or expensive.
- Complexity: 3D printing and CAD technologies can be complicated to work with because there are numerous software tools and techniques used in the creation and fabrication of 3D objects. Additionally, the complicated process of designing can be challenging to manage since the designer needs to be aware of how to use the various tools to develop a quality product.
- Time: The amount of time required to create a car using CAD or 3D printer techniques is often long, as the design process could require several iterations of the design before a product that is successful is designed. Furthermore, the process of fabrication of 3D printing could be an extended process because the printer has to be properly set up as well, and the process of printing may be much longer than standard manufacturing techniques.
- Accuracy: The precision that is achieved by CAD or 3D printer technology is not guaranteed, since there are errors that can occur in the design or the fabrication process that could cause untrue outcomes. In addition, the accuracy in the material used in 3D printing may be limited because certain materials might not reproduce the results you want.
- Safety: The security that comes with CAD or 3D printing techniques could be a problem because some of the materials used in 3D printing are potentially hazardous when not handled properly. Additionally, the security of components made using CAD as well as 3D printing technology could be a problem, since some components might not be sturdy enough to stand up to the stress of driving.
All of them must be considered to produce an effective product.
Conclusion
The importance of 3D printing and CAD within Formula 1 car development has been a game-changer, since it has allowed engineers to create and construct cars more quickly and produce parts that are more precise and long-lasting. Through allowing engineers to swiftly develop and test prototypes, 3D printing and CAD have allowed Formula 1 teams to stay ahead of their competitors and push their cars to a higher benchmark of speed. While technology is continuing to develop, the possibilities of 3D printing and CAD will continue to expand and provide Formula 1 teams with even more freedom to invent and build the lightest, fastest, and most reliable cars that can be found on the road.